At the start of the century, talking to a robot was a Utopian dream – not something common people would ever get to live.
In 2023, it is the norm.
Unless you are living under a rock, you communicate with chatbots on a regular basis. From online bookings to online shopping, issue resolution, and feedback sharing, these chatbots are becoming increasingly common.
In fact, the global chatbot market is expected to hit the $994 million mark by 2024. And chatbots have become a buzzword today.
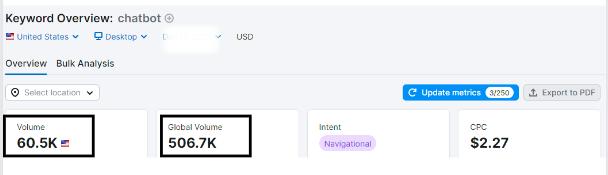
According to SEMRush, Chatbots have an average global search volume of 506.7K and in the US alone, that search volume is around 60.5K.
Every other company has their own chatbot now – either operating on their website or via messaging platforms like WhatsApp, Instagram, Facebook, etc.
But before you start considering chatbot development for your business, you should know…
But what is a chatbot?
How do chatbots work?
What is their need and purpose?
In this blog, we will walk you through the answers to all these questions and more.
Let’s dive in.
What Is A Chatbot?
TechTarget defines chatbots as follow:

Let’s understand it in detail now.
Imagine having a helpful friend who is always ready to chat with you, answer your questions, and assist you with various tasks. Simply speaking that’s what a chatbot is – a friendly computer program designed to talk to you and help you out, just like a friend would.
Technologically speaking, chatbots, short for chat robots, are computer programs designed to simulate natural language conversations with users.
They are an application of artificial intelligence (AI) that processes and interprets user inputs in textual or spoken form.
Chatbots serve a diverse range of purposes, enriching user experiences and streamlining interactions across various domains.
Purpose of Chatbots: Primary Objectives
The primary objectives of chatbots include:
- Provide instant assistance and real-time support.
- Operate 24/7 for continuous accessibility.
- Offer cost-efficient automation of routine tasks.
- Utilize AI for personalized interactions and recommendations.
- Break down language barriers for enhanced accessibility.
- Enhance user engagement through interactive conversations.
- Automate repetitive and rule-based tasks efficiently.
By fulfilling these purposes, chatbots transform digital interactions, making them more efficient, personalized, and enjoyable for users.
ChatGPT is one of the most advanced chatbots available in the market today. It can not just answer queries and give advice, but also write blogs, codes, business plans, movie scripts and whatnot. In fact, its latest version GPT 4 can also process images and give visual outputs.
It wouldn’t be an overstatement to say that ChatGPT is a superbot!
But this was not always the case. Chatbots have come a long way today. From simple rule-based response machines to intelligent bots who can drive sales and resolve grievances, the evolution of chatbots has been an interesting journey.
Let’s take a look at it.
The Evolution Of Chatbots: From ELIZA to Generative AI
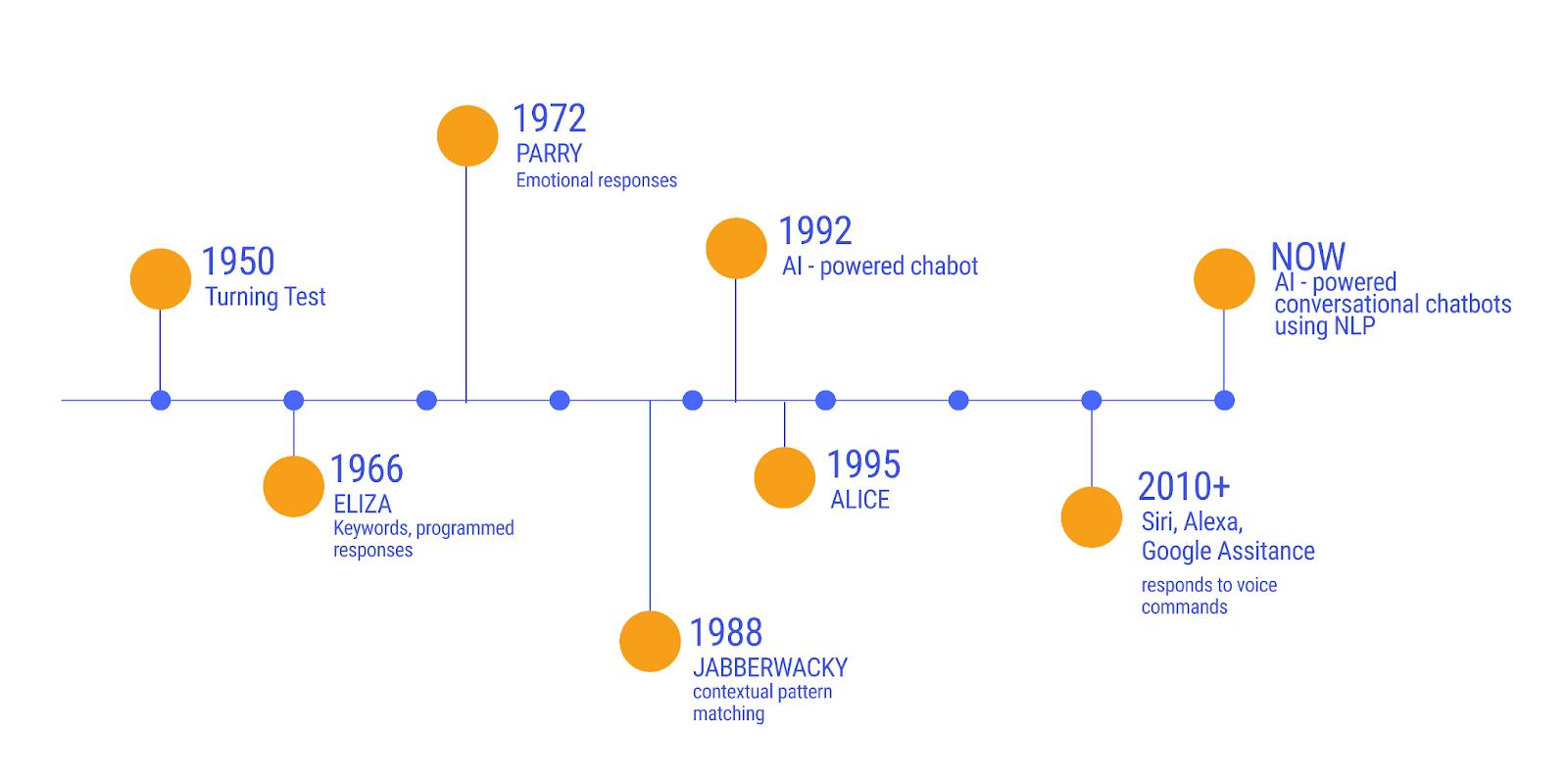
Lets understand the timeline in detail below:
Phase 1: First Generation Chatbots
ELIZA and Basic Chatbots (1960s – 2010s)
Humans have been conversing with computers since the 1960s. Sounds strange, right? But it is true.
Back in the 1960s, Joseph Weizenbaum created ELIZA, the world’s first chatbot.

This early technology, exemplified by ELIZA, A.L.I.C.E., and SmarterChild, was the first generation of chatbots.
These basic or rule-based chatbots used algorithms to detect keywords in user inquiries and offered predetermined responses.
For example, if you asked a question related to weather, these humble bots would pick the keyword “weather” and let you know if you should carry an umbrella or sunglasses.
Many contact centers utilized these chatbots to assist customers with frequently asked questions. And many are still using them today.
These chatbots employ scripted responses and input buttons to guide users’ inquiries.
For instance, a customer service bot might present predefined options like “Change password,” “Order status,” and “Store hours,” responding with scripted information based on the users’ selections.
However, due to the lack of advanced natural language processing (NLP) capabilities, these primitive chatbots often struggle to understand human language and context.
Phase 2: Second Generation Chatbots
Conversational Agents (Early 2010s)
The 2010s marked a significant shift with advancements in machine learning (ML). This lead to the rise of conversational agents.
These agents, including virtual assistants like IBM Watson, Siri, and Alexa, that use advanced NLP and ML capabilities to understand natural language more accurately than their basic predecessors.
They could learn from past interactions, comprehend voice commands, and perform tasks with increased efficiency.
These conversational agents were quickly adopted by businesses across industries to assist both employees and customers.
For instance, in a pharmacy’s interactive voice response system, conversational AI allowed callers to use voice commands to resolve problems and complete tasks. These systems could also detect customer sentiment and escalate calls to live agents if necessary, showcasing a leap in functionality compared to basic chatbots.
Phase 3: Third Generation Chatbots
Generative AI Chatbots (Late 2010s – Present)
In the late 2010s, ML advancements, such as transformer neural networks and large language models (LLMs), paved the way for generative AI chatbots. Some of the trending ones in the market today are Jasper AI, ChatGPT, and Bard.
These chatbots are trained on massive datasets, enabling them to understand natural language better than their conversational agent predecessors.
Importantly, this advanced technology allowed chatbots to generate creative texts, including poems, song lyrics, short stories, and essays, within seconds.
Today, these generative AI chatbots have become invaluable tools for businesses. From creating content to summarizing past customer interactions and drafting email responses, there is hardly anything these smartbots can’t do.
Moreover, they offer human-like interactions, personalizing customer self-service experiences in ways previously unattainable.
The release of ChatGPT in 2022 marked a pivotal moment, sparking widespread interest in generative AI from technology vendors, the general public, and customer experience (CX) professionals alike.
While simpler chatbots handled basic customer service inquiries, generative AI chatbots promised to automate a greater percentage of customer interactions, showcasing the continuous evolution and potential of chatbot technology.
Wondering how it all happens in the backend? Let’s explore how chatbots work.
How Chatbots Work?
Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how modern-day NLP-backed chatbots work.
Step 1: User Input Reception
- Users initiate interaction by providing input through text, voice, or other interactive formats.
- Chatbots receive and process these inputs as the starting point of the conversation.
Step 2: Data Preprocessing
- Raw input undergoes preprocessing to normalize text, remove irrelevant elements, and convert voice inputs into readable text.
- This step ensures that the chatbot works with clean and standardized data.
Step 3: Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Language understanding begins with NLP, which interprets user inputs in the context of the conversation.
- Tokenization breaks down the input into meaningful units, and parsing extracts grammatical structure.
Step 4: Context Management
- Chatbots maintain a memory of past interactions and context to provide coherent and relevant responses.
- Dialog flow control ensures the conversation progresses logically based on the user’s input and the context.
Step 5: Knowledge Base Integration
- If needed, chatbots access knowledge bases or databases to retrieve information relevant to user queries.
- API integration enables dynamic interactions, allowing chatbots to fetch real-time data or perform specific tasks.
Step 6: Response Generation
- Rule-Based Systems: Basic chatbots use predefined rules and decision trees based on detected keywords to generate responses.
- Machine Learning Models: Advanced chatbots leverage machine learning algorithms to generate responses, learning from past interactions.
Step 7: User Interface Integration
- Depending on the platform, chatbots have graphical interfaces with buttons or operate purely through text-based interfaces.
- Some chatbots integrate voice recognition systems to process spoken commands and queries.
Important: Learning and Adaptation
- ML-based chatbots undergo training on large datasets to enhance their understanding and response generation capabilities.
- Chatbots may incorporate user feedback to continually learn and adapt, improving their overall performance over time.
Now that we have understood the what, why, and how of chatbots, it is time to dive deeper and understand the importance of chatbots in modern business, the various use cases, and how you can get a chatbot developed for your business.
We will cover all these topics in our upcoming blogs. So keep checking back this space for updates and subscribe to our newsletter to get notified about new blogs!